Introduction:

The world relies on precise machinery, from the engines that power our cars to the delicate instruments used in medical procedures. But how do we ensure these machines are perfectly aligned for optimal performance? Enter laser alignment, a powerful tool that uses the accuracy of lasers to achieve just that.
What is Laser Alignment?
Laser alignment is a technique that utilizes a laser beam to establish precise straightness, parallelism, or angularity between machine components. By directing a laser beam along a machine’s shaft or other critical elements, any misalignments become evident as the beam deviates from its intended path.
Why is Laser Alignment Important?
Improper machine alignment can lead to a cascade of problems:
- Increased wear and tear: Misaligned components grind against each other, causing premature wear and tear, leading to costly repairs and replacements.
- Reduced efficiency: Misalignment can cause friction and drag, reducing a machine’s overall efficiency and increasing energy consumption.
- Poor product quality: Inaccurate alignment can lead to vibrations and inconsistencies in the manufacturing process, resulting in products that don’t meet specifications.
Benefits of Laser Alignment:
Laser alignment offers numerous advantages over traditional alignment methods:
- High precision: Lasers provide an incredibly accurate reference point, allowing for precise alignment adjustments.
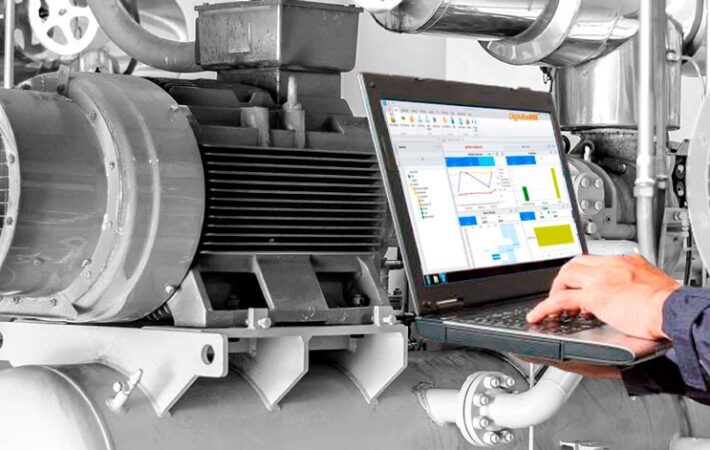
- Ease of use: Modern laser alignment tools are user-friendly and often come with intuitive interfaces.
- Time-saving: Laser alignment can significantly reduce the time needed to align machinery compared to traditional methods.
- Improved safety: By minimizing the need for manual adjustments near moving parts, laser alignment enhances safety in the workplace.
Getting Started with Laser Alignment:

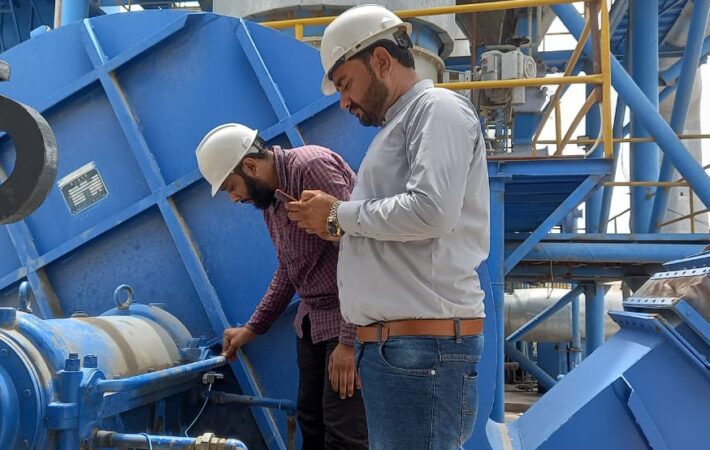
The specific steps involved in laser alignment will vary depending on the machinery and the type of laser alignment tool being used. However, here’s a general overview:
- Preparation: Secure the laser emitter and detector onto the designated mounting points on the machine.
- Alignment Procedure: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to project the laser beam onto the corresponding target on the machine.
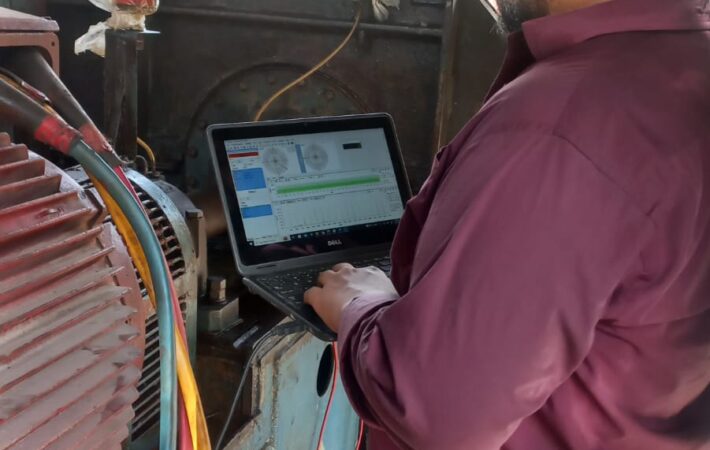
- Adjustment: Based on the laser beam’s position on the target, make adjustments to the machine’s components until the beam hits the center of the target.
- Verification: Once adjustments are made, repeat the procedure to verify that the alignment is within the specified tolerance.
Laser Alignment Tools:
There are various types of laser alignment tools available, each catering to specific needs:
- Shaft Alignment Systems: These systems are used to align rotating shafts, a common application in machine tools and industrial equipment.
- Line Lasers: Line lasers project a straight line, ideal for aligning components that require a straight path, such as guide rails or conveyor belts.
- Dot Lasers: Dot lasers project a single red or green dot, useful for aligning components that require precise positioning, like pulleys or bearings.
Conclusion:

Laser alignment is a valuable tool for anyone who wants to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of their machinery. By understanding the basics and employing the appropriate tools, you can reap the numerous benefits of laser alignment and keep your machines running smoothly.
Additional Tips:
- Always refer to the user manual for your specific laser alignment tool.
- Invest in proper safety gear, such as safety glasses, when working with lasers.
- If you’re dealing with complex machinery, consider seeking professional assistance for laser alignment tasks.
By incorporating laser alignment into your maintenance routine, you can contribute to a more efficient, cost-effective, and safer work environment.







Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *